Term life insurance is a clear and reasonable kind of life coverage that provides monetary insurance for a predefined period, or “term.” Assuming that the policyholder dies during this term, a demise benefit is paid to the recipients. This advantage can assist with covering costs like home loans, training, or day-to-day residing costs, guaranteeing monetary security for friends and family.
Dissimilar to extremely durable disaster protection, term approaches don’t create cash esteem and are simply centered around providing inclusion. Strategy terms regularly range from 10 to 30 years, with expenses staying level throughout the length. Term disaster protection is excellent for those looking for reasonable inclusion customized to explicit monetary commitments or periods.
What Is Term Life Insurance?
Term life coverage is a disaster protection strategy that provides a demise benefit to the policyholder’s beneficiaries, assuming that they die within a foreordained period (the “term”). Typical term lengths include 10, 20, or 30 years, although different choices are available. Assuming the policyholder endures the term, the inclusion lapses and no advantage is paid out.
Unlike extremely durable disaster protection, such as whole life or widespread life, term life doesn’t increase cash esteem over the long run. It is, therefore, principally intended to give a substantial passing advantage to a minimal expense during a particular period, which can be great for families or people with transitory monetary commitments.
How Does Term Life Insurance Work?
Term life coverage works by giving monetary security to the safeguarded for a particular period. The policyholder pays charges to the insurance agency in return for inclusion. These charges are ordinarily fixed for the length of the strategy term, making it more straightforward for policyholders to make a financial plan.
If the policyholder dies during the approach’s term, the insurance agency pays the passing advantage to the recipients recorded in the arrangement. If the safeguarded endures the term, no benefit is paid out, and the approach lapses.
There are two primary components of term life insurance:
- The Premium: The amount the policyholder must pay to maintain coverage. Premiums are typically lower than those for permanent life insurance policies because term life insurance only covers the insured for a limited period and does not accumulate cash value.
- The Death Benefit: The amount of money that will be paid to the beneficiaries upon the death of the insured, provided it occurs within the term of the policy.
Key Features of Term Life Insurance
There are several essential features to consider when exploring term life insurance:

- Term Length: Term life insurance policies are available in varying lengths, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years, although terms as short as 5 years or as long as 40 years may also be available. The length of the policy should align with costs or other long-term debts.
- Level vs. Decreasing Term Life Insurance: Level Term: With a level term policy, the death benefit remains the same throughout the policy. This ensures that the beneficiaries receive a consistent payout, regardless of how much time has passed.
- Decreasing Term: A decreasing term policy is one where the death benefit decreases over time. These policies are often used for specific financial obligations, such as a mortgage or loan, where the debt decreases over time, and the policy’s payout is designed to match the decreasing balance.
- Renewability: Some term life insurance policies offer a renewal feature, which allows the policyholder to extend the term at the end of the coverage period, typically without the need for a medical exam. However, the premiums will often increase significantly upon renewal as the insured individual is older and more likely to face health challenges.
- Convertibility: Many term life policies come whole life or universal life) at some point during the term. This conversion can usually be done without the need for a medical exam, which may be particularly useful if the policyholder’s health changes during the term.
- Affordability: Term life insurance is often the most affordable type of life insurance because it only provides death benefits and doesn’t accumulate any cash value. This makes it an attractive option for people who need substantial coverage but may not be able to afford the higher premiums associated with permanent life insurance.
Advantages of Term Life Insurance
There are several reasons why term life insurance may be the right choice for specific individuals or families:
- Affordability: Term life insurance is typically much more affordable than whole life or universal life insurance. This makes it an ideal option for individuals who need substantial coverage but are on a budget.
- Simplicity: Term life insurance is straightforward to understand. It is a bet between the policyholder and the benefit. If the policyholder survives, the insurance company keeps the premiums.
- Flexibility: Term life policies can be tailored to specific financial needs. For instance, a young family might choose a 20-year term to cover their children’s education and living expenses, while someone nearing retirement might opt for a 10-year term to cover the remaining years of a mortgage.
- Temporary Coverage: For individuals who only need life insurance for a certain period—such as during the years they have young children, a mortgage, or business debts—term life insurance offers the coverage they need without committing to a lifelong policy.
Disadvantages of Term Life Insurance
While term life insurance offers many advantages, it also has its drawbacks:
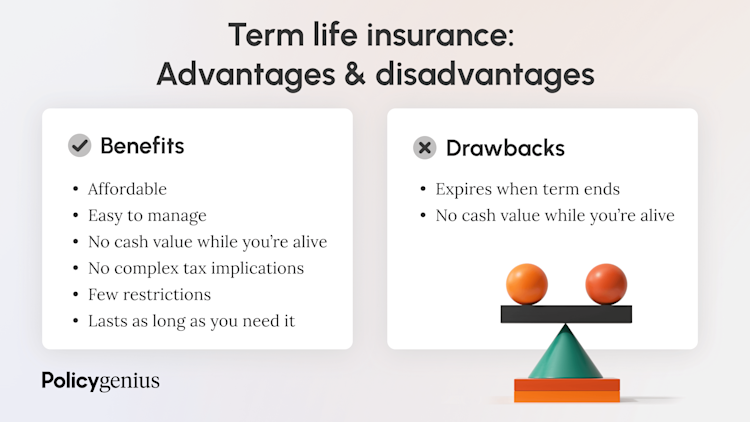
- No Cash Value: Unlike whole life or universal life insurance, term life policies do not accumulate cash value over time. This means that the policyholder is paying for coverage without building any equity or investment.
- Limited Coverage Period: The most significant limitation of a specific period. Receive no benefit, and they may face higher premiums if they seek to renew the policy at an older age.
- Premiums May Increase: If the policyholder renews the premiums, they may increase substantially. This is because the policyholder is now older, and the risk of death has increased.
- No Payout If You Outlive the Term: If the policyholder outlives the term of the policy, there is no payout, and the premiums paid during the term are essentially “lost” in the sense that no benefit is received.
Who Should Consider Term Life Insurance?
Term life insurance can be an excellent choice for various groups of people, including:
- Young Families: Parents with young children and significant financial responsibilities, such as mortgages or education expenses, may find term life insurance to be a cost-effective way to ensure their family’s financial security in the event of their death.
- People with Short-Term Obligations: Individuals who have temporary financial obligations, such as paying off student loans, mortgages, or business debts, may benefit from term life insurance that covers them during the life of these obligations.
- People Who Want Affordable Coverage: Those who want a high level of life insurance coverage but don’t have the budget for more expensive permanent life insurance options should consider term life insurance.
- Those Looking for Flexibility: Term life insurance is a good option for those who need temporary coverage and may want to explore permanent life insurance later in life.
How to Choose the Right Term Life Insurance Policy
Choosing the proper term life insurance policy requires careful consideration of your financial situation and long-term goals. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:

- Amount of Coverage: Consider how much coverage you need. Typically, financial advisors recommend a policy that will replace 10 to 12 times your annual income, but this amount can vary depending on your obligations and goals.
- Term Length: The length of the term should match the period during which you will have significant financial responsibilities. For example, if you have young children and a mortgage, a 20 or 30-year term might make sense.
- Premiums: Make sure the premiums fit within your budget. While term life is generally more affordable than permanent life insurance, it’s still essential to ensure that you can afford the premiums throughout the term.
- Riders and Add-Ons: Many term life policies offer benefits. Determine whether these additional features will be beneficial to you.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the term disaster protection?
Term extra security is a kind of life coverage that includes a predefined period, or “term.” Assuming the policyholder kicks the bucket during this period, the guarantor pays a demise advantage to the assigned recipients.
How, in all actuality, does the term disaster protection work?
The policyholder pays everyday expenses for the picked term (e.g., 10, 20, or 30 years). Assuming the policyholder dies during the term, the recipients get the settled-upon-death benefit.
What happens when the term closes?
When the term closes, the inclusion stops. A few strategies offer choices to reestablish, convert to super durable insurance, or let the contract pass.
Who ought to think about the term disaster protection?
It’s excellent for people who are looking for reasonable inclusion to meet explicit monetary commitments, such as paying off a home loan, subsidizing instruction, or supporting wards.
What amount does it cost?
Term disaster protection is, generally, more reasonable than perdurable life coverage costs depending on factors such as age, well-being, term length, and inclusion sum.
Does the term extra security have monetary esteem?
No, term extra security doesn’t collect money esteem. It is planned exclusively to give a passing advantage.
Should I alter my term strategy?
Indeed, numerous backup plans offer riders, for example, benefits for essential sickness or incidental demise to improve the arrangement’s inclusion.
What are the advantages of term extra security?
It offers effortlessness, reasonableness, and adaptability, making it an excellent choice for transitory monetary insurance.
Conclusion
Term life coverage is a practical method in case of your passing during a predetermined term. It’s beneficial for those with transitory monetary commitments, like bringing up youngsters, taking care of a home loan, or covering different obligations. While it misses the mark on cash esteem gathering and the long-lasting inclusion of highly durable disaster protection, term life offers a direct and reasonable method for getting your family’s future. While picking a term life coverage strategy, it’s vital to survey your necessities cautiously, think about the perfect proportion of inclusion and term length, and contrast choices from various backup plans to guarantee you’re getting the best worth.




